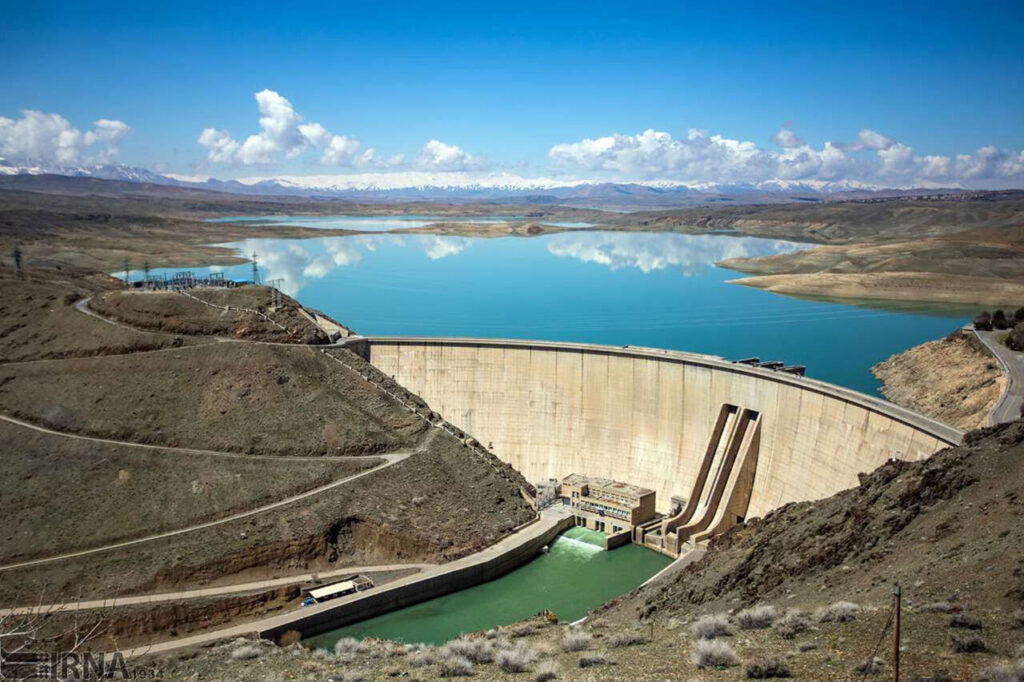
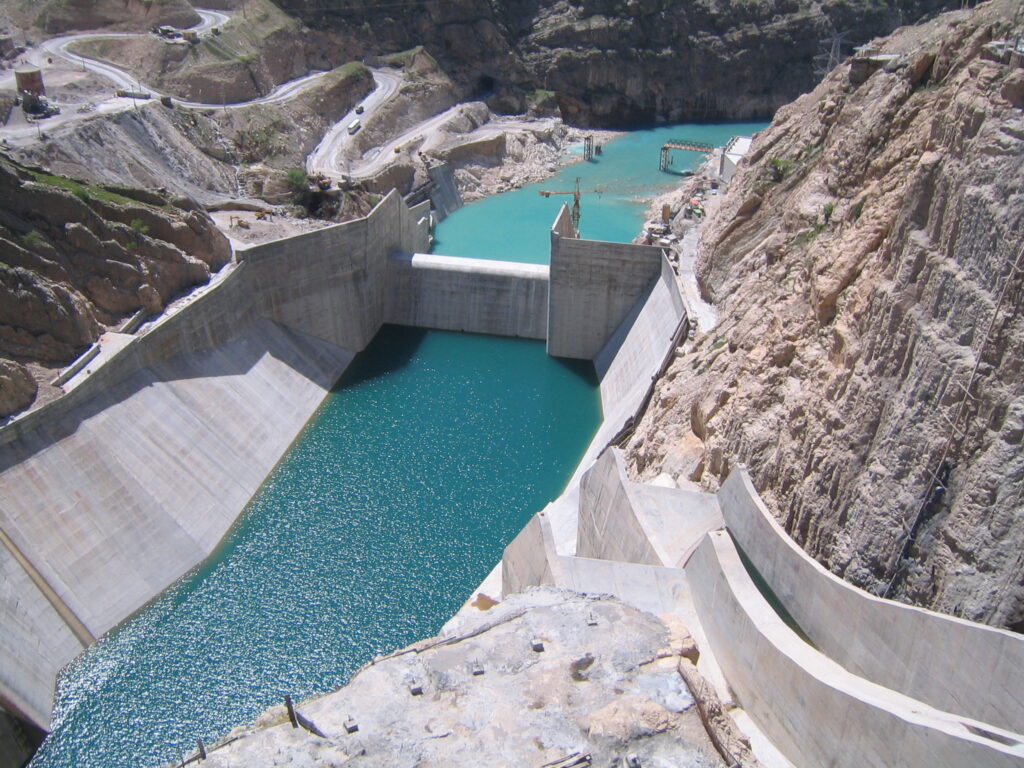
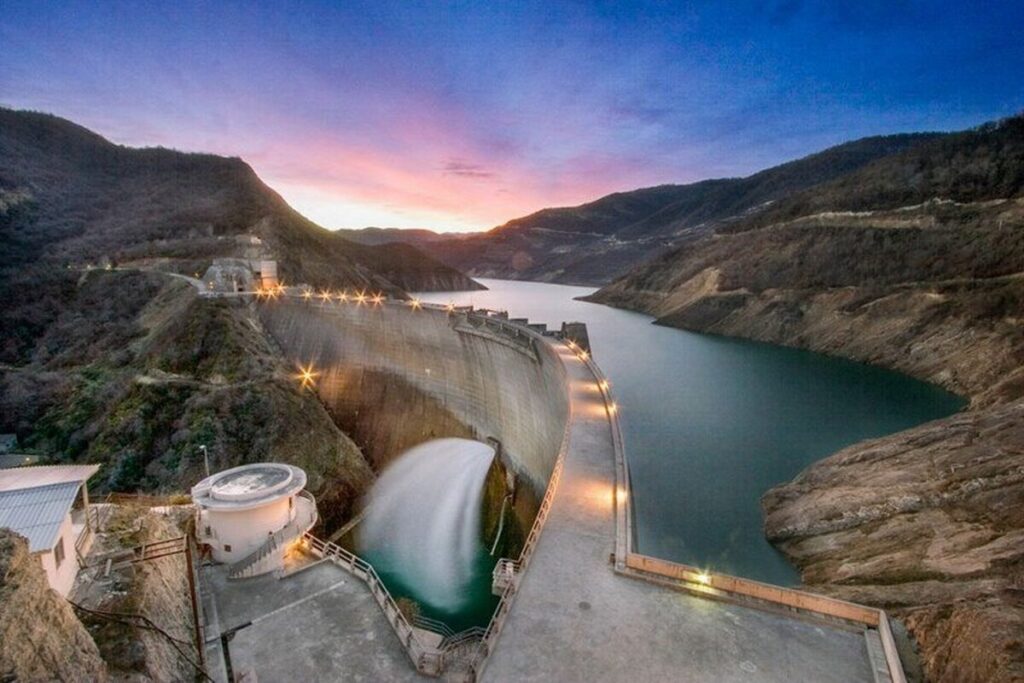
The Seimare Dam, situated on the seimare River in southwestern Iran’s Ilam Province, is a pivotal infrastructure project aimed at hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and regional water supply. Completed in 2013, this 180-meter-high arch dam boasts a reservoir capacity of 3.2 billion cubic meters and supports a 480 MW underground powerhouse equipped with three 160 MW Francis turbines. The project was developed by the Iran Water and Power Resources Development Company (IWPRDC), with Perlite Company serving as the main contractor.
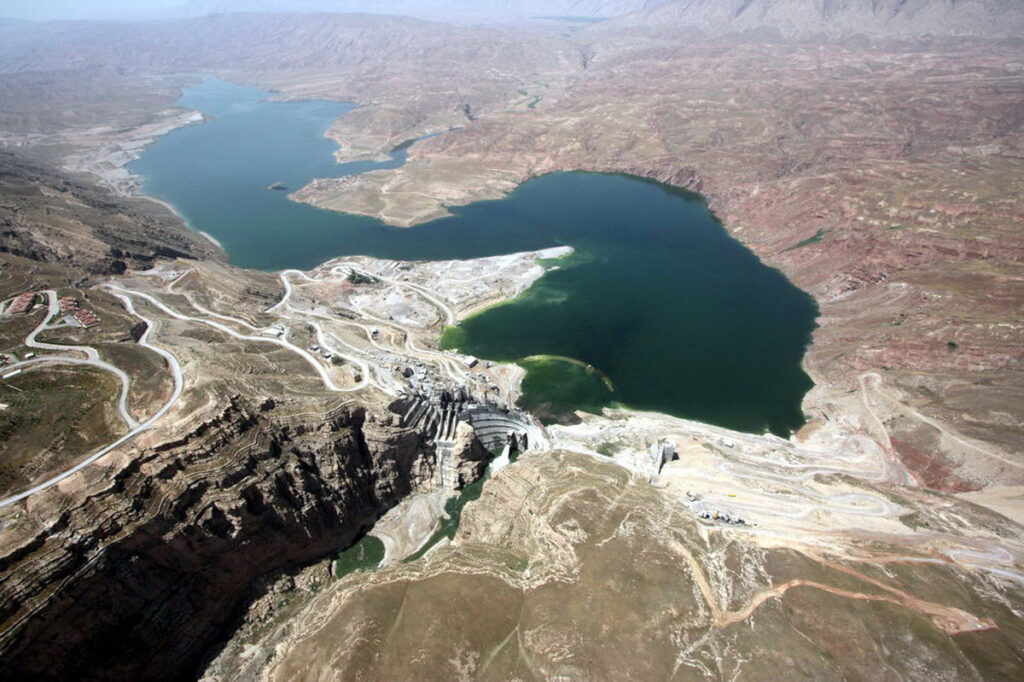

Dam Specifications: 180 m high, 202 m crest length, 550,000 m³ concrete volume.
Reservoir Capacity: 3.2 billion m³, covering 69.5 km² and extending 40 km in length.
Power Generation: 480 MW capacity, producing approximately 850 GWh annually.
Flood Management: Equipped with main and auxiliary spillways capable of discharging up to 8,230 m³/s.
Advanced Engineering: Utilized grout curtains and extensive grouting (120,000 m drilled) for foundation stabilization.
Strategic Location: Located on the Seymareh River, a key tributary of the Karkheh River, enhancing water flow regulation to downstream systems.
Iran Water and Power Resources Development Co
Ilam Province,
Iran
The Challenge
The Seimare Dam & Hydropower Project, located on the Seimare River in western Iran, involved a 180 m-high rock-fill dam with a clay core, designed to generate approximately 480 MW of electricity. The project faced significant geotechnical and hydraulic challenges, including variable rock conditions, potential landslides in steep valleys, and high sediment loads in the river. The design of the diversion tunnels, spillways, and powerhouse caverns had to account for seismic activity in the region, water pressure fluctuations, and long-term stability of both dam and underground structures. Ensuring minimal environmental impact while providing reliable flood management and energy production added further complexity.
What did RMTEC do
RMTEC applied advanced geotechnical and hydraulic engineering methods to address these challenges. Detailed site investigations, rock mechanics analyses, and numerical modeling guided the design of dam foundations, tunnels, and spillway structures. Optimized lining and support systems were implemented in diversion tunnels and underground caverns to handle high water pressures and seismic loads. RMTEC also developed sediment management and flood control strategies, while coordinating construction sequencing and monitoring programs to maintain safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance.
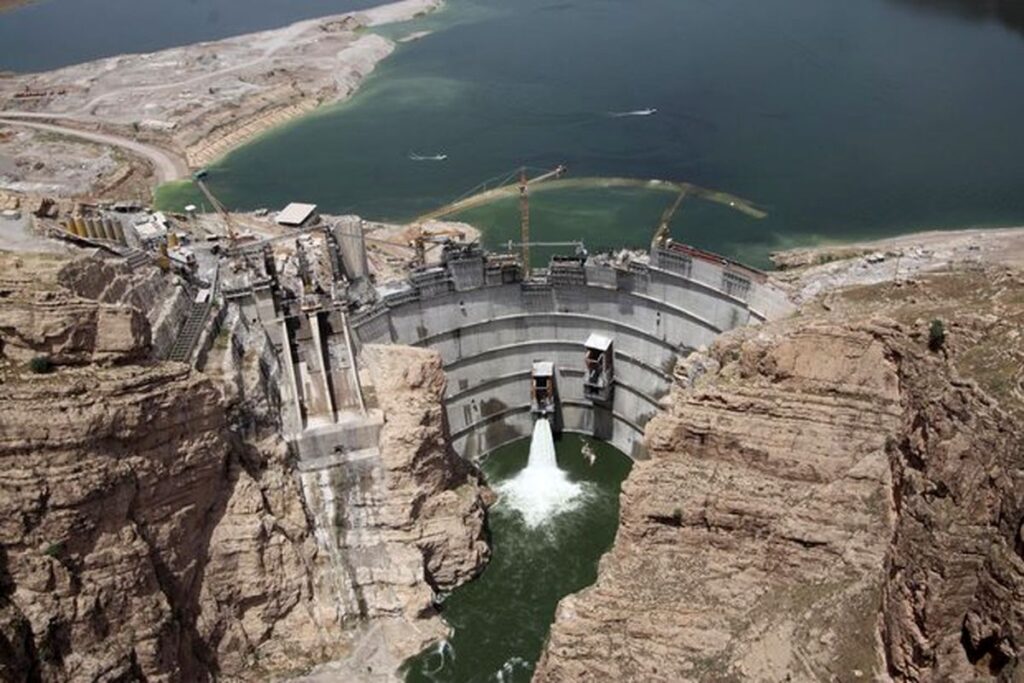

The Results
- 480 MW reliable hydropower generation
- Stable dam and underground structures in seismic zones
- Effective flood and sediment management
- Enhanced water supply and regional development